Introduction
The SS31 peptide, also known as elamipretide, has emerged as a promising therapeutic agent targeting mitochondrial dysfunction, a key factor in aging, neurodegenerative diseases, and metabolic disorders. Mitochondria are essential for cellular energy production, and their impairment contributes to various chronic conditions. SS31 has demonstrated the ability to protect and restore mitochondrial function, making it a potential breakthrough in treating mitochondrial-associated diseases. This article delves into the structure, mechanism of action, therapeutic applications, clinical research, and future potential of SS31 peptide.
Structure and Properties of SS31 Peptide
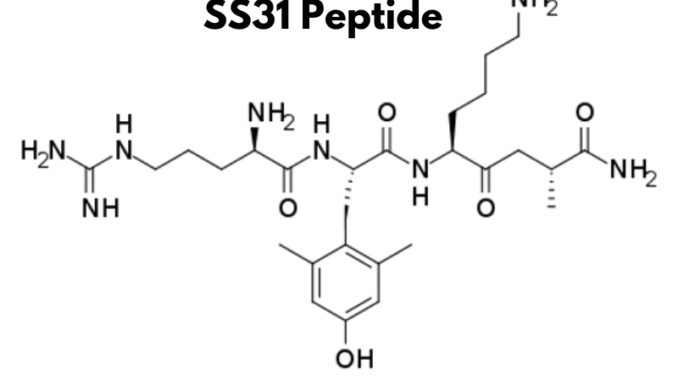
SS31 peptide is a small, cell-permeable tetrapeptide with the sequence D-Arg-Dmt-Lys-Phe-NH2 (Dmt stands for 2,6-dimethyltyrosine). It belongs to a class of synthetic mitochondria-targeting peptides designed to selectively interact with mitochondrial membranes and counteract oxidative stress.
Key properties of SS31 include:
- Selective Mitochondrial Targeting: SS31 preferentially accumulates in the inner mitochondrial membrane, where it interacts with cardiolipin, a crucial phospholipid essential for mitochondrial structure and function. This selectivity ensures that the peptide effectively reaches its site of action, making it more efficient than other general antioxidants that lack specificity.
- Antioxidant Action: Unlike conventional antioxidants, SS31 directly neutralizes reactive oxygen species (ROS) at the source by stabilizing cardiolipin and reducing mitochondrial oxidative damage. By preventing lipid peroxidation, SS31 helps maintain the structural integrity of the mitochondrial membrane.
- Cell Permeability: Due to its unique structure, SS31 efficiently crosses cell membranes and reaches intracellular mitochondria, enhancing its therapeutic efficacy. This property is particularly valuable because many potential mitochondrial-targeted therapies fail to reach their intended site due to cellular barriers.
Mechanism of Action
SS31 functions primarily through its interaction with cardiolipin in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Cardiolipin plays a vital role in maintaining mitochondrial architecture and facilitating electron transport chain (ETC) function. The key mechanisms through which SS31 exerts its effects include:
- Cardiolipin Stabilization: SS31 binds to cardiolipin, preventing its peroxidation and preserving mitochondrial integrity. Cardiolipin is essential for the proper function of mitochondrial proteins, including components of the ETC, which are crucial for ATP production.
- Reduction of Oxidative Stress: By neutralizing ROS and inhibiting lipid peroxidation, SS31 reduces mitochondrial damage, which is critical in aging and degenerative diseases. Mitochondria are major sources of ROS, and excessive ROS production leads to oxidative stress, damaging cellular structures and accelerating disease progression.
- Enhancement of ATP Production: By protecting mitochondrial function, SS31 improves ATP synthesis, which is essential for cellular energy metabolism. Mitochondrial dysfunction results in energy deficits, which are linked to numerous diseases, including neurodegeneration and muscle wasting.
- Inhibition of Apoptosis: SS31 prevents mitochondrial dysfunction-induced cell death by stabilizing mitochondrial membranes and preserving cytochrome c localization. Apoptosis, or programmed cell death, is often triggered by mitochondrial damage and is implicated in many degenerative conditions.
- Mitigation of Inflammation: Reduced mitochondrial oxidative stress leads to lower levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which contributes to the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases. Mitochondrial dysfunction has been linked to inflammation in conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes.
Therapeutic Applications of SS31
SS31 has demonstrated potential in treating a range of diseases associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. Below are some key areas of research and clinical application:
1. Neurodegenerative Diseases
Mitochondrial dysfunction is a hallmark of neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Studies have shown that SS31 can:
- Protect neurons from oxidative stress and apoptosis by preserving mitochondrial function, thereby reducing neuronal loss.
- Improve mitochondrial energy production in brain cells, which is crucial for maintaining cognitive function and preventing neurodegeneration.
- Reduce neuroinflammation and improve cognitive function by lowering oxidative damage and enhancing mitochondrial resilience.
- Potentially slow disease progression in conditions such as Alzheimer’s by preserving synaptic integrity and neurotransmission.
2. Cardiovascular Diseases
Mitochondria play a critical role in maintaining cardiac function. SS31 has shown promise in treating heart-related disorders, such as:
- Heart Failure: SS31 improves mitochondrial efficiency in cardiomyocytes, enhancing cardiac contractility and function. Heart failure is often linked to mitochondrial dysfunction, leading to energy deficits in heart cells.
- Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: By reducing ROS-induced damage, SS31 protects the heart during events such as heart attacks and surgical procedures. Ischemia-reperfusion injury occurs when blood supply returns to tissue after a period of ischemia (lack of oxygen), causing oxidative stress.
- Hypertension: Studies suggest SS31 may help mitigate high blood pressure by preserving endothelial function and reducing oxidative stress. Hypertension is associated with endothelial dysfunction, which SS31 may counteract through its mitochondrial-protective properties.
3. Muscle Disorders and Sarcopenia
Aging and chronic diseases often lead to muscle atrophy due to mitochondrial dysfunction. SS31 has been shown to:
- Improve muscle strength and endurance by enhancing ATP production in muscle cells, leading to better performance and reduced fatigue.
- Reduce mitochondrial damage in aging skeletal muscles, which is crucial for preventing sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss).
- Enhance exercise tolerance in patients with mitochondrial myopathies, conditions that impair muscle energy metabolism.
4. Diabetes and Metabolic Disorders
Mitochondrial impairment contributes to insulin resistance and metabolic disorders. SS31’s ability to enhance mitochondrial function can:
- Improve insulin sensitivity by restoring energy homeostasis in insulin-responsive tissues.
- Reduce oxidative stress in pancreatic beta cells, which is critical for maintaining insulin secretion and preventing diabetes progression.
- Prevent complications such as diabetic nephropathy and neuropathy by protecting mitochondria in vulnerable tissues.
5. Kidney Diseases
Mitochondrial dysfunction is implicated in chronic kidney disease (CKD) and acute kidney injury (AKI). Preclinical studies indicate that SS31 can:
- Reduce oxidative stress in kidney cells, thereby preserving renal function and delaying disease progression.
- Improve renal function and reduce fibrosis, a key factor in CKD progression.
- Protect against drug-induced nephrotoxicity, which is a common side effect of certain medications.
Clinical Research and Trials
Several preclinical and clinical studies have investigated SS31’s efficacy and safety:
- Animal Studies: Preclinical models have consistently demonstrated SS31’s benefits in reducing mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and tissue damage in various disease models.
- Human Trials: Early-phase clinical trials have shown SS31 to be well-tolerated with potential benefits in conditions like heart failure, mitochondrial myopathies, and age-related muscle decline.
- Ongoing Research: Further trials are underway to evaluate SS31’s efficacy in neurodegenerative diseases, kidney disease, and metabolic disorders, with the potential to expand its use to other conditions.
Potential Challenges and Future Directions
While SS31 shows immense promise, there are some challenges to consider:
- Long-Term Safety and Efficacy: Although initial trials suggest SS31 is safe, long-term studies are needed to assess its chronic use.
- Optimal Dosage and Delivery Methods: Determining the most effective dosing regimen remains an area of research.
- Regulatory Approval: SS31 is still undergoing clinical evaluation, and obtaining regulatory approval will depend on the outcomes of large-scale trials.
Despite these challenges, SS31 holds significant potential as a mitochondrial-targeting therapy. Future research may expand its applications to other diseases linked to mitochondrial dysfunction, such as cancer and autoimmune disorders.
FAQs
1. What is SS31 peptide?
SS31 peptide, also known as elamipretide, is a small synthetic peptide designed to target mitochondria and protect against oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction.
2. How does SS31 work?
SS31 binds to cardiolipin in the inner mitochondrial membrane, stabilizing its structure, reducing oxidative stress, improving ATP production, and preventing cell death.
3. What diseases can SS31 potentially treat?
SS31 has shown promise in treating neurodegenerative diseases, cardiovascular diseases, muscle disorders, metabolic syndromes, and kidney diseases, all of which are linked to mitochondrial dysfunction.
4. Is SS31 available for clinical use?
SS31 is still under clinical investigation, with early-phase trials demonstrating safety and efficacy in some conditions. It has not yet received regulatory approval for widespread use.
5. Are there any side effects of SS31?
Clinical trials have reported that SS31 is generally well-tolerated, but further research is needed to confirm long-term safety and potential side effects.
See Also: Ztec100.com Tech
Conclusion
SS31 peptide represents a groundbreaking approach to treating diseases rooted in mitochondrial dysfunction. As ongoing research continues to validate its efficacy, SS31 could pave the way for novel mitochondrial-based therapies, offering hope for millions affected by chronic and age-related diseases.

Leave a Reply